Ze Chen, Wenqian Xie, Sven Kranz, Haizheng Hong, Dalin Shi
Limnology and Oceanography
https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.12780
Published: 17 January 2025
Abstract
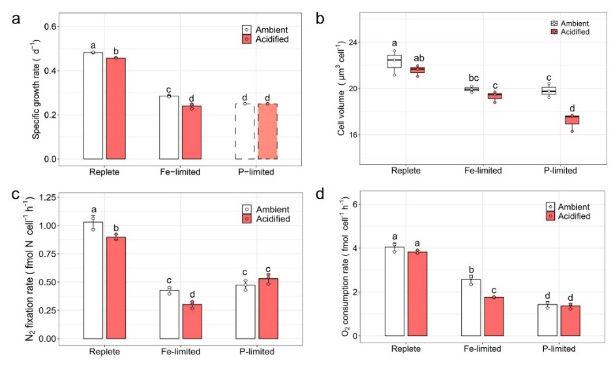
Iron (Fe) and phosphorus (P) availability constrain the growth and N2 fixation of diazotrophic cyanobacteria in the global ocean. However, how Fe and P limitation may modulate the effects of ocean acidification on the unicellular diazotrophic cyanobacterium Crocosphaera remains largely unknown. Here, we examined the physiological responses of Crocosphaera watsonii WH8501 to CO2 enrichment under both nutrient-replete and steadily Fe- or P-limited conditions. Increased CO2 (750 μatm vs. 400 μatm) reduced the growth and N2 fixation rates of Crocosphaera, with Fe limitation intensifying the negative effect, whereas CO2 enrichment had a minimal impact under P limitation. Mechanistically, the high CO2 treatment may have led to a reallocation of limited Fe to nitrogenase synthesis to compensate for the reduction in nitrogenase efficiency caused by low pH; consequently, other Fe-requiring metabolic pathways, such as respiration and photosynthesis, were impaired, which in turn amplified the negative effects of acidification. Conversely, under P limitation, CO2 enrichment had little or no effect on cellular P allocation among major P-containing molecules (polyphosphate, phospholipids, DNA, and RNA). Cell volumes were significantly reduced in P-limited and high CO2 cultures, which increased the surface : volume ratio and could facilitate nutrient uptake, thereby alleviating some of the negative effect of acidification on N2 fixation. These findings highlight the distinct responses of Crocosphaera to high CO2 under different nutrient conditions, improving a predictive understanding of global N2 fixation in future acidified oceans.